Will async/await replace Result Type?
It may not completely replace, but soon you will have less usage of Result Type in codebase.
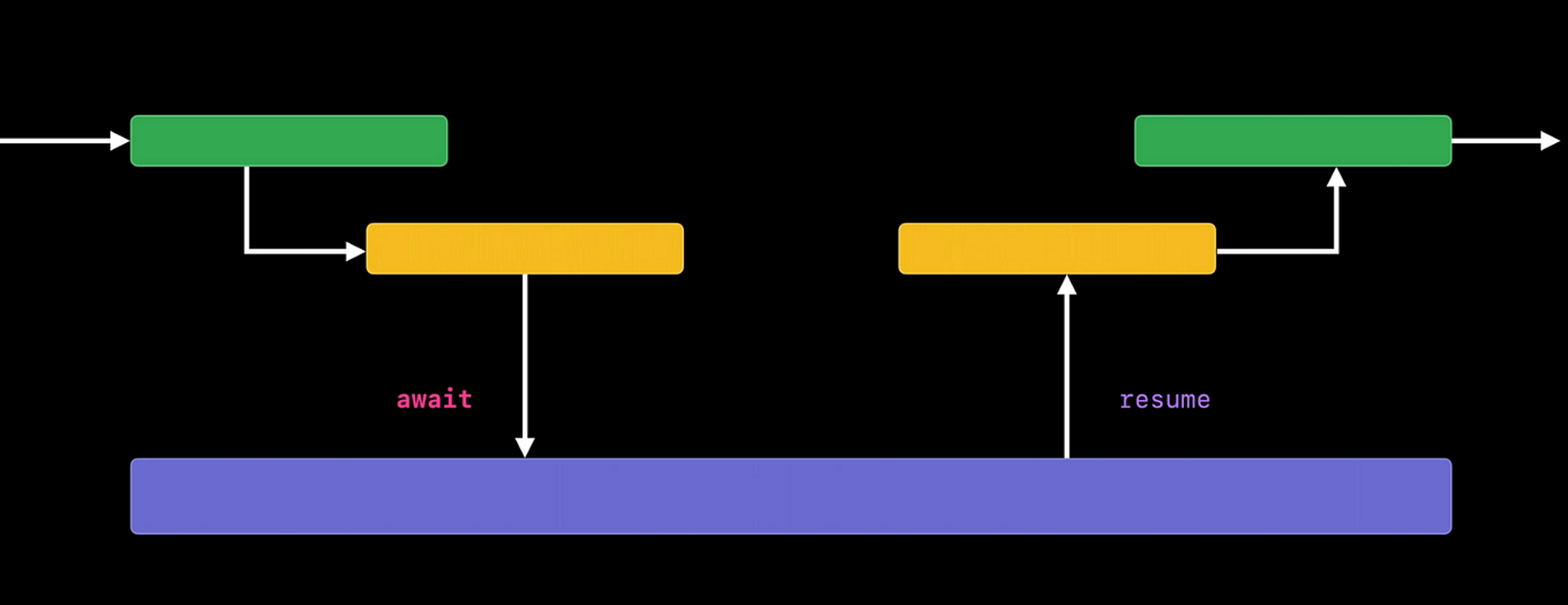
How async/await works in Swift, Courtesy: Apple WWDC
Earlier we used to write 2 optional values in a closure, on the consumer side need to check which one has value and then process using if else condition.
func fetchContent(completion: ([Model]?, Error?) -> Void) {
// perform data request
}Function with a completion handler
With Result Type in place this boilerplate got reduced and we could elegantly handle success and failure. Still code looks messy when we have another pending request based on current api response. As the calls get nested and nested….., it can become a problem when it comes to readability. You can take action and move every “pyramid floor” into its own function, but that’s more of a patch. Till now we talked about callback based concurrency, let’s see how can we use async/await api for concurrency which is supported from iOS 13.
async/await allows us to write asynchronous code just as we write regular code.
async/await facts
asyncenables a function to suspend
awaitmarks where an async function may suspend execution, other work can happen during a suspension
Once an awaited async call completes, execution resumes after the await.
When async/await is more useful?
Let’s say you have a complex asynchronous block of code and on success or failure you have to call completion block. In that situation async/await can simplify code and there will be less chances of forgetting to call completion block.
Completion handler to async/await
func fetch<T: Codable>(request: APIData, basePath: String, completionHandler:@escaping ((Result<T, Error>) -> Void)) { }Function with a completion handler of Result Type
can become
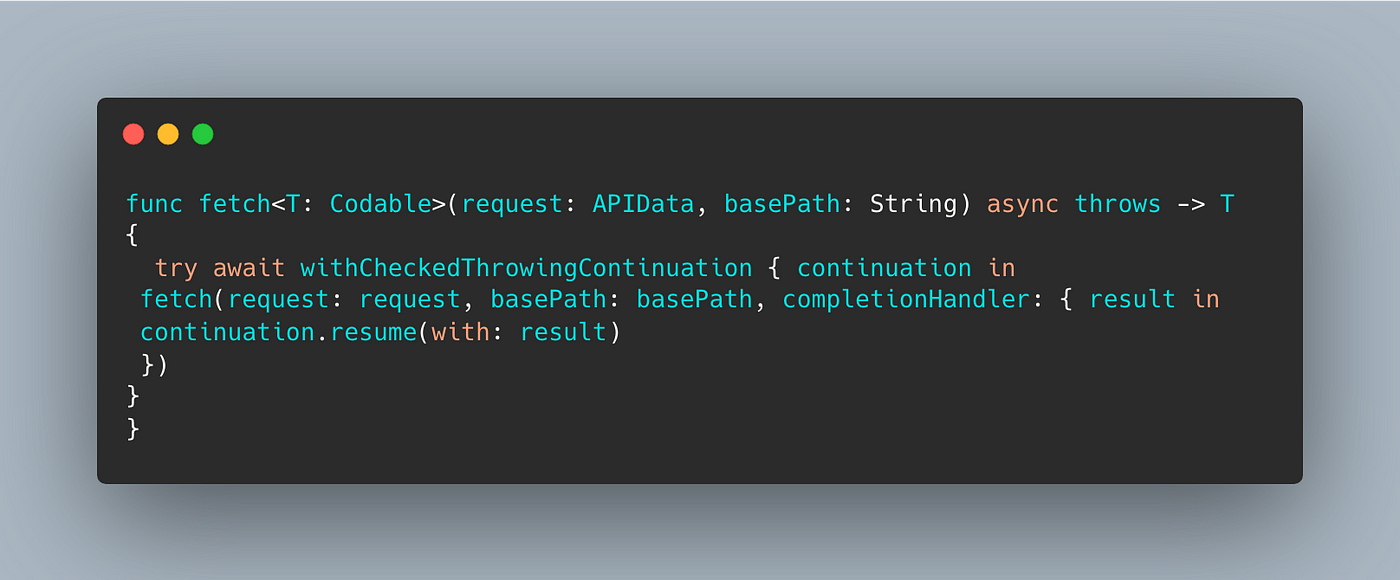
Completion handler of Result Type to async/await
Here we just wrapped existing closure in withCheckedThrowingContinuation to return T. There are multiples variants of resume
Condition of using Continuations is Continuation must be resumed exactly once on every path.
public func resume<Er>(with result: sending Result<T, Er>) where E == any Error, Er: Error
public func resume(returning value: sending T)
public func resume(throwing error: E)Different flavours of resuming a Continuation
If you just want to handle happy case then you can wrap closure in withCheckedContinuation as well.
On client side we can have something like this:
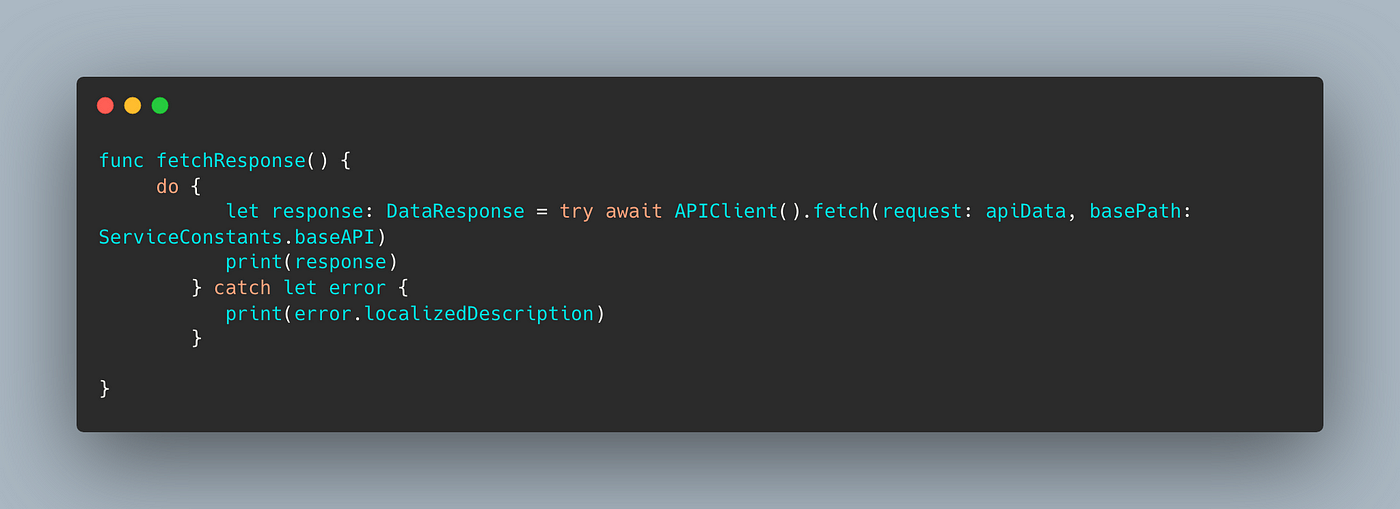
Using async/await client side
If we have nested dependent apis then also code will look simpler.
Now let’s look into how to call this function from Controller/View Model
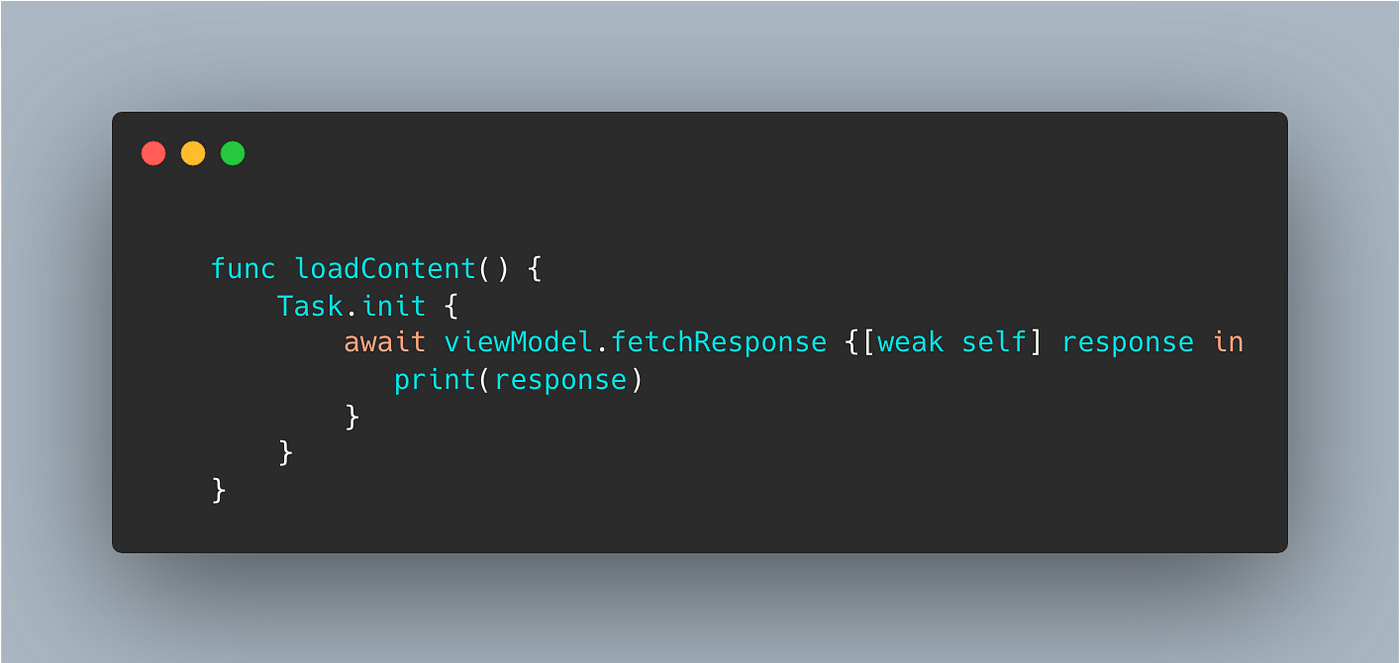
Using async/await Controller/ViewModel side
A Task allows us to create a concurrent environment from a non-concurrent method, calling methods using async/await.
Some useful articles if you wanna go into details:
Meet async/await in Swift - WWDC 2021
This is a free third party commenting service we are using for you, which needs you to sign in to post a comment, but the good bit is you can stay anonymous while commenting.